Quality and safety are a responsibility of everyone in the food chain and not just the manufacture. Beyond the marketing, there are consumers who buy and consume the products. They too are responsible for the quality and safety in many ways. The industry actors act under guidelines and regulations imposed upon their activities. These are the regulatory bodies which also have a key role in ensuring that actors act in a manner that they produce high quality and safe food products.
The overall responsibility for food quality and safety is therefore shared by all segments of the food system, including the various food industry sectors, government regulatory agencies, and the consumers (Figure 1).
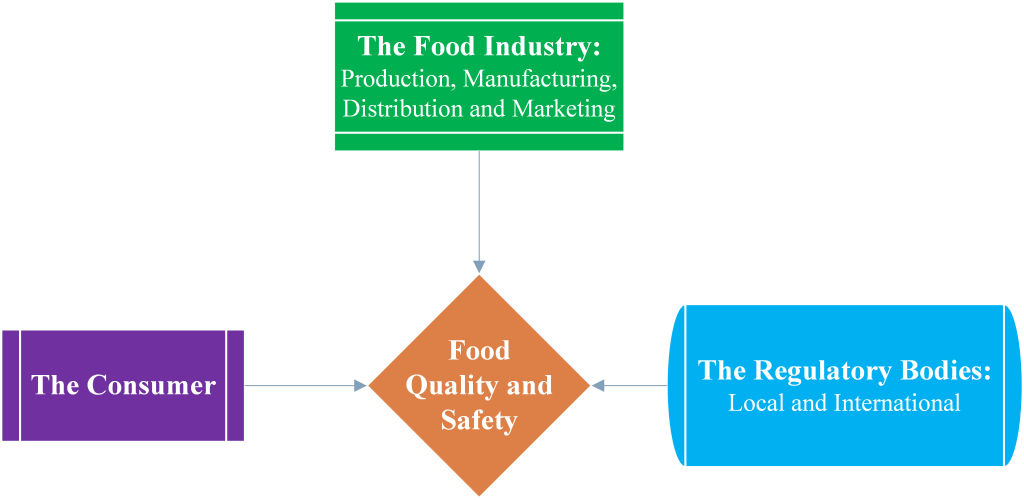
The role of the food industry in assuring food quality and safety
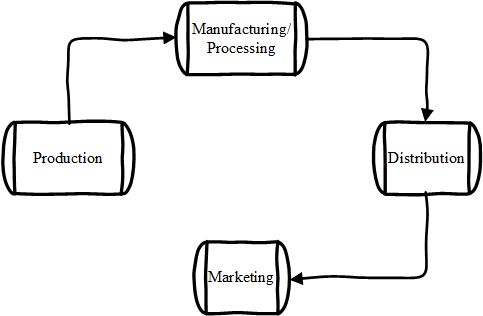
To understand the role of the food industry, it is important to understand what the food industry is made up of. The food industry is divided into four parts as shown in Figure 2.
- Production – Produces raw materials for industries. It includes farming, ranching, aquaculture, fishing, and orchard management.
- Manufacturing – Converts raw agricultural materials to more refined or finished products. Requires many input operations and processes that are key in ensuring food quality and safety.
- Distribution – Concerns itself with aspects that are conducive to product sales e.g. storage stability, storage requirements, product form, weight, bulk and transportation.
- Marketing – Selling of food and food products; wholesale, retail, restaurants, institutional etc.
Everyone involved at any part in the food industry is responsible for the quality and safety of the food, either directly or indirectly.
Production
Production sector is tasked with production of raw materials for the manufacturing sector. These are mostly farmers or plant and animal-based products. Raw materials are expected to be of high quality and safety. The quality and safety can be compromised in many ways. For instance:
- Livestock farmers selling diseased animals for slaughter or animals undergoing treatment before the withdrawal period is over. This poses the possibility of having antibiotic residues in the meat. Such meat may not be safe. Similarly, farmers may sell milk before the withdrawal period is over which will result in having antibiotic residues in milk.
- Apiary keepers may produce adulterated honey while fisheries may present fish contaminated with heavy metals among other contaminants.
- Crop producers may present crop produce which is contaminated with pesticide residues, mycotoxins such as aflatoxins in maize and putulin in fruits, or heavy metals and other industrial wastes. If the farmer grew their vegetables near a dumpsite, the vegetables have potential for contamination with not only heavy metals and industrial wastes but also microbial pathogens.
This shows that the producers are very crucial in ensuring that high quality and safe foods are produced. There is so much that can go wrong and therefore this sector must uphold high integrity and transparency to ensure that the food is suitable for human consumption.
Can all contaminants be reduced by processing?
Although processing has potential for enhancing safety, not all contaminants can be reduced by processing. In addition, not all products from this sector are designed for processing. Most of it is consumed with minimal or no processing at all. This makes it very crucial since contaminants found in the food may end up on the consumers plate shortly after. Nevertheless, even though processing may deal with contaminants especially the vegetative microbial contaminants, it may not alter the chemical contaminants to warrant the safety of food. Thus, the poor quality of raw materials presented at the manufacturer’s reception platform will affect the quality and safety of the final product.
Therefore, to ensure that the production sector does well in presenting high quality materials to the manufacturers, the manufacturers and other stake holders have to hold producers accountable to the quality of produce they present. Manufacturers must demand only the best from the producers.
Good agricultural practices and Good manufacturing practices
The production sector should ensure the application of good manufacturing practices in the quest for high food quality and safety. Good manufacturing practices guidelines for different producers have been produced by various organizations such as those outlined by the Food and Agriculture Organization for family agriculture [6].
Good agricultural practices as well as good manufacturing practices and good distribution practices are a collection of standards, legislation, and technical guidelines applicable to the production, processing , and transportation of food, addressing human health care, the conservation of the environment, and the improvement of worker and family conditions [6].
Good agricultural practices may include:
- Conditions important in enhancing the working conditions for all workers. E.g. Sufficient training, social security systems, emergency preparedness – first aid kits available, having adequate personal protective equipment; Changing rooms, toilets, etc.
- Personal hygiene for all persons is also important. Facilities to facilitate this must be available to allow for the operators to wash as often as required.
- Farmers have to know the place to plant and what to plant at any place. They should know the history of the farm and recognize fertile lands with sufficient water. Contaminated field such as waste disposal areas should, MUST be avoided. The most probable diseases and pests in the region should also be known.
- With support from a qualified person, the soil should be analyzed to determine its condition and the type of crop that is suitable for the area. Avoidance of soil erosion is important. Crop rotation is required.
- Handling of crops should in such a manner that produce the best quality output. Starting with high quality seeds that are resistant to diseases is a good place to begin. Coming up with pest management strategies especially those that do not involve the use of chemicals is highly advisable e.g. Push and Pull Technology. The density, transplant processes and protection of the crops are also very crucial.
- Adequate use and management of water is important to avoid wastage and ensure that crops receive adequate, optimum levels. Water used should be potable and not contaminated like in the case of waste water. If waste is to be utilized or redirected for irrigation, it must be treated.
- Use of agro-chemicals should be minimized and controlled. They should be applied with strict instructions from experts. Whenever biological controls are available, they should be most preferred. Application should be done while wearing protective attire. Proper record keeping is mandatory to avoid harvesting contaminated products. Storage of these chemicals should also be done carefully to avoid contamination or reach by unauthorized persons and children. Empty containers and packaging materials should be disposed adequately to avoid re-use.
- What fertilizer to use and the quantities should be adequately be determined. Nowadays there are soil scanners that can advice on the quantities for a particular soil given its actual composition. Framers should seek such services from qualified practitioners. The application and storage should be done adequately.
- Use of organic manure should also be done adequately. This is critical as it may carry contaminants including pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli (O157:H7).
- Domestic, production and work animals should be well taken care of, Adequate feeding and disease management. This is critical as there are zoonotic diseases that can be passed to human beings.
- Harvesting should be done carefully depending on the product to ensure high quality products are obtained. For instance, milk can be contaminated if the under is dirty or the farmers hands are contaminated. Fruits can be bruised accelerating contamination and spoilage.
- Storage and transport of the harvested materials has to be done in a manner to ensure no cross contamination occurs. Preservation practices geared towards ensuring the freshness of the product should be employed.
- For products meant for immediate sale to consumers or manufacturers, freshness is key.
- Farmers can establish a traceability system for their produce to better control production issues.
- Proper and adequate record keeping is a MUST.
Benefits of Good Agricultural Practices
The Good Agricultural Practices have the following benefits:
- The farmers, manufacturers and consumers all get to receive high quality and safe food produce.
- Improved workers health as agricultural chemicals are used properly
- Improved food and nutrition security for the farmer and the consumers
- Protection for the environment as no chemicals will contaminate the soils
- Protection of biodiversity since chemicals do not harm the non-target organisms
- Animal welfare guaranteed as they receive adequate feeding and care
- Sustainability and new markets for high quality premium produce for farmers
- Increased income for farmers
- Better control of production practices



