The manufacturing sector obtains inputs from the producers and transforms them into finished products through a number of ways. The processing techniques used by various manufacturers are different and therefore yields different results regarding the quality and safety of the products. All said, the initial quality and safety of the raw material inputs may determine the end product quality. Thus, high quality and safe raw materials are required since contaminated ones may result in contaminated end products. Thus, the producers must do their job right for the manufacturers to achieve their objectives.
Manufacturers must have way of ensuring that the raw materials they receive from the producers are of the quality they desire. This calls for quality testing and surveillance for the producers by the manufacturers. This means that the manufacturer must be aware of what the producers or farmers are doing to have the raw materials. Some manufacturers have taken control of the production systems just to make sure that they get the raw materials of their desirable quality.
Assuming that the raw materials received by manufacturers are of good quality, the manufacturer has a role to play in ensuring the quality and safety of the final end products. Among the guidelines that the manufacture should strive to implement are the good manufacturing practices (GMPs). Besides the GMPs, the manufacture may opt to implement other quality and or safety management systems guidelines such as ISO 9000 and ISO 22000 that have been proposed to support the processors to achieve food quality and safety.
Processing involves a multitude of activities or operations before the final products are ready for storage or dispatch as shown in Figure 3. Any of these steps has potential to enhance or degrade food quality. Similarly, the safety of the food may also be impaired. Therefore, care must be taken to ensure that all these steps are done in a way that enhances the quality and safety of the food. To achieve this, basic hygiene and safety practices can be applied through the implementation of the GMPs.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs)
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) are a framework of guidelines developed to ensure that food products are reliably manufactured and regulated to quality and safety standards that are put in place. These are designed to reduce the risks associated with any production of food products that cannot be eliminated by testing the end product. They thus, cover all manufacturing aspects from raw material, facilities and equipment to personnel training and personal hygiene. They are therefore, the minimum sanitary and processing requirements necessary to ensure the production of high quality and safe food products. They are directed towards preventing food contamination as well as cross contamination. They are a baseline, minimum requirement, for there to be safe food. It is a requirement, or prerequisite for other safety systems such as the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system [7].
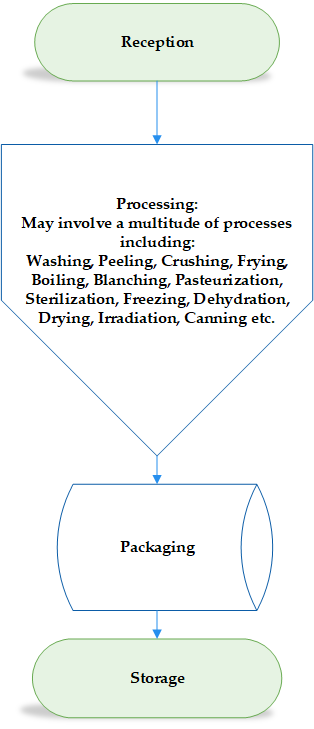
Figure 3. The processing chain – a general example
Its key to recognize that it is a legal requirement for the manufacturer to produce and deliver high quality and safe food products to the consumer. Thus, although some of these guidelines are not mandatory, they are important in ensuring adherence to food quality and safety standards and regulations.
Reception
At reception, the manufacturer must confirm that the raw materials they receive from producers meet their minimum requirements. There should be no compromise as the quality and safety of raw materials has an implication on the quality and safety of the final product. Care must be takes as contamination as well as cross contamination may take place at this stage.
Processing
Processing stages are many and diverse for various products. Processing has potential to enhance the safety of the product if it is well carried out and controlled. For instance, raw milk may potentially carry Mycobacterium tuberculosis which is destroyed upon pasteurization at 72 oC for 15 seconds. Nevertheless, contamination may also occur if pasteurized product comes into contact with raw materials or contaminated surfaces.
Packaging
Packaging may become a nightmare as it may introduce foreign matter into the supposedly safe product. Improper packaging may also present an avenue for contamination from the environment.
Storage
Storage must be done adequately to assure the safety of food. Food that require refrigeration should be stored under such conditions without temperature abuse as that has potential for spoilage and the development of unsafe outcomes.
This clearly shows that the manufacture is tasked with so much responsibility of ensuring the final product is of high quality and safety. Nevertheless, as mentioned earlier, there are guidelines to support them to achieve this. Among those guidelines are the GMPs, HACCP and ISO standards.
GMPs include various activities
The following is a list of the basic food safety controls [7] applicable to most processors:
- Plant environment and facilities
- Production equipment and machinery
- Raw materials and ingredients
- Quality assurance
- Storage and delivery
- Employee training and personal hygiene
- Cleaning and sanitation
- Pest control
- Recordkeeping and traceability
Each safety control has to be addressed adequately to ensure quality and safety of the final products. For example, the various activities covered by the GMPs include guidelines on how the design of the facility should be. For instance, the material used for walls, elevation of the floors, drainage, etc. The activities may also include the processes set forth for handling of raw materials, design of equipment, hygiene and sanitation practices, personal hygiene practices as well as control of pests in the factory. Thus, GMPs cover activities for each of the nine safety controls all with the aim of limiting food contamination and cross contamination. This is crucial in the pursuit of food quality and safety. GMPs are prerequisite to the implementation of safety management systems such as HACCP and ISO 22000 which have been hailed for their sufficiency in ensuring food safety for the end products. Thus, it is the role of the manufacturer to do everything they can to improve the quality and safety of the final food. In so doing, it is expected that they not only implement GMPs but also strive to implement HACCP and ISO 22000 Food Safety Management Systems.